The Frog Class 5 English Complete NCERT Solution Notes Santoor Book
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 English Chapter 5 The Frog (Santoor Textbook)
Here are full NCERT Textbook solutions for Class 5 English – “The Frog” Santoor / NCERT Chapter 5 .
Class 5 English Chapter 5 The Frog Summary
The poem “The Frog” describes the life of a frog. It lives both in water and on land. As a tadpole, it lives only in water, but as an adult frog, it hops and leaps on land. The frog eats insects by flicking its long sticky tongue. Its webbed feet help it swim fast. The frog croaks loudly, especially after rain. Its skin colour helps it hide among plants and leaves, but it must always be careful of snakes.
New Words and Meanings
- Hop – to jump lightly on both feet
- muddy — full of or covered with mud
- Flick – quick, sharp movement
- Damp – slightly wet
- dew — tiny drops of water that form on cool surfaces, especially at night
- beware — be cautious of; guard against something
- Croak – rough sound of a frog
- Webbed – having skin between the toes for swimming
- Camouflage – blending with surroundings to stay safe
Class 5 English Chapter 5 The Frog NCERT Questions and Answers
Here are full NCERT solutions including Question answers given in textbook for Class 5 English – “The Frog” (Santoor / NCERT Chapter 5).
Let Us Think
Q1. Where does the frog like to sit or spend time?
Answer: The frog likes to sit in ponds and damp places, especially during rainy season.
Q2. How does the frog catch its food?
Answer: It catches insects by flicking its long sticky tongue.
Q3. How does the frog move in water and on land?
Answer:
- In water, it swims with its webbed feet.
- On land, it hops and leaps with its strong legs.
Q4. What helps the frog hide in its surroundings?
Answer: The frog’s skin colour matches with plants and leaves, helping it to camouflage.
Think and Discuss
Q1. What would it feel like to live like a frog, both in water and on land?
Answer: It would be exciting because we could swim and hop easily, but also challenging to face predators and changes in surroundings.
Q2. If you could hop as high as a frog, what fun things would you do?
Answer: I would jump over walls, touch tree branches, and play hopping games with friends.
Q3. How is a frog’s life different from a fish’s life?
Answer:
- A fish lives only in water; a frog can live on land and in water.
- A fish uses gills to breathe; a frog uses lungs and skin.
- A frog can hop on land, but a fish cannot.
Q4. How are frogs’ webbed feet similar to flippers used by divers?
Answer: Both help in swimming by pushing water more effectively.
Let Us Learn
A. Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
( Choose the correct words from the brackets and fill in the blanks. )
- My colours match the plants …………… trees. (because/or)
- Would you like to learn about frogs …………… tadpoles? (because/and)
- I hop around happily, …………… I must watch out for snakes! (but/so)
- Frogs swim easily …………… they have webbed feet. (or/and)
Answer:
- My colours match the plants and trees. (or/and)
- Would you like to learn about frogs and tadpoles? (because/and)
- I hop around happily, but I must watch out for snakes! (but/so)
- Frogs swim easily because they have webbed feet. (because/or)
B. Rearranged sentences: Choose correct option
( The following words have been rearranged into sentences. Choose the correct option. )
- hunts/night/the/silently/tiger/at
Options:
a. The tiger hunts silently at night.
b. Tiger hunts the silently at night.
c. Hunts the tiger at night silently. - elephants/in/forests/live/large/groups/in
Options:
a. Elephants live large in groups forests.
b. In groups large, elephants live in forests.
c. Elephants live in large groups in forests. - web/a/spider/carefully/its/weaves
Options:
a. A spider carefully weaves its web.
b. Spider carefully weaves its web a.
c. Carefully a spider weaves web its. - crocodile/waits/the/silently/riverbank/the/near
Options:
a. Crocodile waits the silently the near riverbank.
b. The silently crocodile waits near the riverbank.
c. The crocodile waits silently near the riverbank. - a/swims/turtle/slowly/in/ocean/the
Options:
a. A turtle swims slowly in the ocean.
b. Swims turtle slowly an ocean in.
c. The ocean swims a slowly turtle in.
Answers:
- The tiger hunts silently at night.
- Elephants live in large groups in forests.
- A spider carefully weaves its web.
- The crocodile waits silently near the riverbank.
- A turtle swims slowly in the ocean.
Let Us Speak (Page 58-59)
A. Tongue twisters — Practice:
( Three tongue twisters are given below. Try speaking each tongue twister slowly at first. Gradually increase your speed with each repetition. Count how many times you can say it correctly without making a mistake. )
- Four fierce frogs fight for flies.
- Fast frogs flip-flop across fluffy fields.
- Funny frogs flap floppy feet.
B. Listen and repeat — Pairs of words your teacher says, you repeat.
Your teacher will say aloud the following pairs of words. Listen carefully and repeat each pair.
bet bat
set sat
men man
leg lag
met mat
Let us Listen
My Frog’s World
Your teacher will read out instructions for you to follow and create your own ‘Frog’s World’ in the space provided on the next page.
- Draw the place: Imagine a place where your frog might be happy, like a pond, a forest or a rainy area.
- Draw your frog: Draw a frog in the above setting.
- Decorate with words: Around your drawing, write some words from the poem that describe the frog’s life. You can even write your own short sentence about the frog’s world.
- Colour it: Use colours to bring your frog’s world to life! Be creative and make it as colourful as you would like.
Do it Yourself
Let Us Write
Here is a message for you from Hopper, the frog.
Dear Reader,
Hello! I am Hopper. I am writing this message to you from my big lily leaf pad. I like splashing water when it rains. My favourite hobby is sitting in water puddles and croaking. I love eating mosquitoes and other insects. What do you like to do?
Your friend,
Hopper
Write a reply to Hopper, the frog.
Answer:
Dear Hopper,
Thank you for your lovely message from your lily pad. I also enjoy splashing in water and playing in the garden after rain. I like reading stories under trees. Do you enjoy croaking loudly after rain? Stay safe from snakes.
Your friend,
[Your Name]
Did You Know?
How is a frog different from a toad?
Frogs usually have smooth, moist skin, and long legs for hopping, while toads have dry, rough, bumpy skin, and shorter legs for walking or hopping.
Which is our national aquatic animal?
It’s the Ganges river dolphin! It cannot see well, so it uses sounds to find its way in the water!
Let us Do

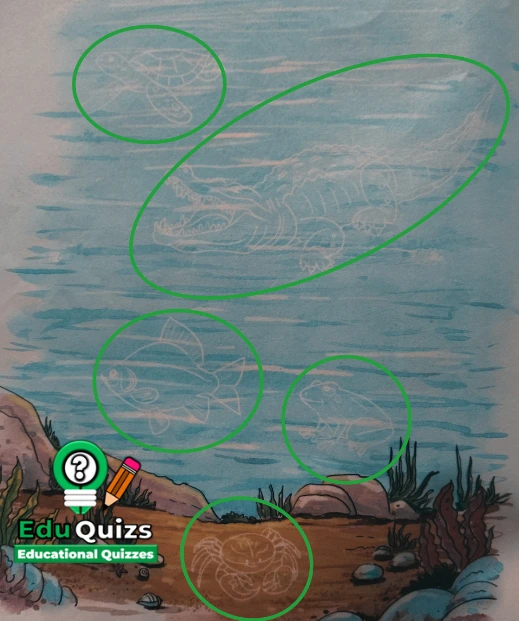
A. Five of us are hiding in the picture. Can you find us?

B. Look at the following steps carefully and draw a duck in the given space.
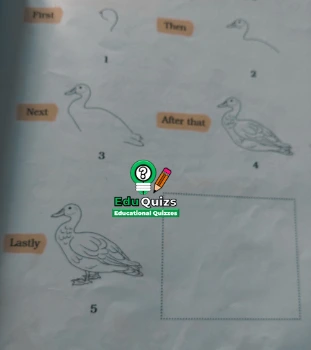
Do yourself follow instruction given in the above image
C. Move three crayons to change the direction in which the fish is swimming.

Answer Hint : move red number 1 crayon and put above front and then number 3 blue crayon above it and now last number 2 at last as shown in the image below.
Note: watch colors of crayons carefully to identify moves in image as we show with numbers

Let us Explore
Choose any two of the below and find out a few facts about them.

Answer:
Puffer Fish
- The puffer fish can inflate its body like a balloon when it feels threatened.
- It has spines that stick out when it puffs up to scare away enemies.
- Some puffer fish are poisonous, and their toxin can be very dangerous.
Starfish
- A starfish usually has five arms, but some can have more.
- It can regrow a lost arm — that’s called regeneration.
- Starfish move using tiny tube feet on their underside.
Jellyfish
- Jellyfish have no bones, brain, or heart — they are made mostly of water.
- They move by pulsing their bell-shaped bodies through the water.
- Some jellyfish can glow in the dark under the sea!
Octopus
- An octopus has eight arms called tentacles.
- It can squirt ink to escape from predators.
- The octopus is very intelligent and can even open jars to get food.
Seahorse
- The male seahorse carries the eggs and gives birth to the babies!
- They swim upright, unlike most fish.
- Seahorses hold onto sea plants using their curly tails.
Catfish
- Catfish have whisker-like feelers near their mouths called barbels.
- They live mostly in rivers and ponds.
- Catfish are bottom feeders — they eat food from the riverbed.
FAQs on Class 5 English Poem The Frog
The poem shows the unique life of a frog – how it lives in water and on land, eats insects, and protects itself. It reminds us that every creature has special qualities and an important role in nature.
Q1. Who is the poet of “The Frog”?
The poem is adapted from a traditional description of the frog’s life, focusing on nature study.
Q2. What is the main food of a frog?
Frogs eat insects, which they catch with their long tongue.
Q3. Why is a frog called an amphibian?
Because it can live both on land and in water.
Q4. How does a frog protect itself from enemies?
It camouflages with plants and leaves and stays alert to avoid snakes.
